Inverted vulva in dogs, also known as recessed vulva or hypoplastic vulva, is a condition where the vulva is positioned further into the body than normal. This can lead to various health issues and discomfort for your furry companion. It’s important to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this condition to ensure your dog’s well-being.
What Causes an Inverted Vulva in Dogs?
Several factors can contribute to an inverted vulva. One of the most common causes is genetics. Certain breeds, such as Bulldogs, Pugs, and Shar-Peis, are predisposed to this condition due to their conformation. Obesity can also play a significant role, as excess fat tissue can obscure the vulva. Hormonal imbalances, especially low estrogen levels, can also contribute to the development of an inverted vulva, particularly in spayed females.
Sometimes, an inverted vulva may be present from birth (congenital). In other cases, it can develop later in life due to factors like weight gain or hormonal changes. Understanding the underlying cause is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Recognizing the Symptoms of an Inverted Vulva
The primary symptom of an inverted vulva is the recessed appearance of the vulva itself. It may appear as a small slit or be almost completely hidden by surrounding skin and fur. This can lead to several secondary issues, including:
- Recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs): The recessed vulva can trap bacteria and urine, creating a breeding ground for infection.
- Skin irritation and inflammation: Urine scalding and bacterial overgrowth can cause redness, itching, and discomfort around the vulva.
- Difficulty urinating: In severe cases, the inverted vulva can obstruct urine flow.
- Vaginitis: The recessed vulva can increase the risk of vaginal infections.
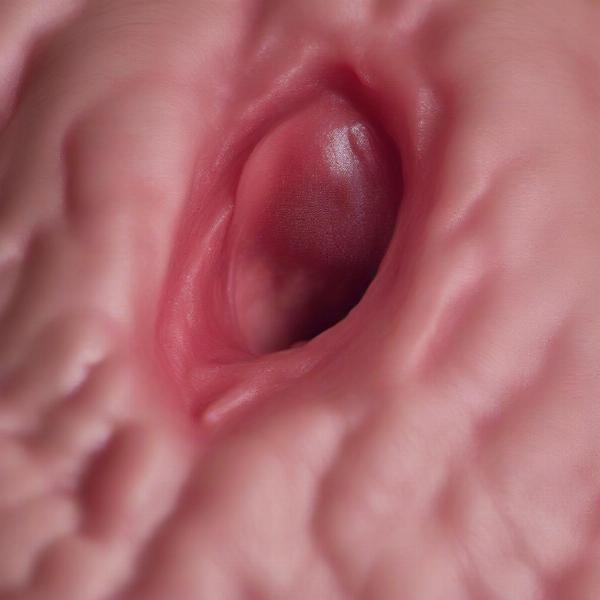 Symptoms of Inverted Vulva in Dogs
Symptoms of Inverted Vulva in Dogs
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult a veterinarian for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Inverted Vulva in Dogs
Treatment for an inverted vulva depends on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. For mild cases, managing the dog’s weight and maintaining good hygiene around the vulval area can be sufficient. Regular cleaning with warm water and a mild antiseptic solution can help prevent infections.
In more severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary. A vulvoplasty is a surgical procedure that repositions and reconstructs the vulva to a more normal position. This helps reduce the risk of infections and improves the dog’s comfort.
Living with an Inverted Vulva: Long-Term Care
Even after surgical correction, ongoing care is essential to prevent recurrence and maintain the dog’s health. This includes:
- Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial to prevent the vulva from becoming recessed again.
- Regular hygiene: Cleaning the vulval area regularly can prevent infections.
- Veterinary check-ups: Regular veterinary visits are essential to monitor the dog’s condition and address any potential complications.
Conclusion
Inverted vulva in dogs can be a concerning condition, but with proper diagnosis and management, you can ensure your furry friend lives a comfortable and healthy life. Regular veterinary check-ups and proactive care are key to preventing complications and ensuring your dog’s well-being. Remember to consult your veterinarian for any concerns about your dog’s vulvar health.
FAQ
- What breeds are most prone to inverted vulva? Bulldogs, Pugs, and Shar-Peis are among the breeds most commonly affected.
- Can spaying cause an inverted vulva? While spaying itself doesn’t directly cause it, the hormonal changes associated with spaying can contribute to its development.
- Is surgery always necessary for inverted vulva? Not always. Mild cases can often be managed with weight control and hygiene.
- What are the long-term risks of an untreated inverted vulva? Untreated inverted vulva can lead to chronic UTIs, skin infections, and discomfort.
- How can I prevent my dog from developing an inverted vulva? Maintaining a healthy weight for your dog is one of the most important preventative measures.
- What is the recovery time after vulvoplasty surgery? Recovery typically takes a few weeks, with specific instructions provided by your veterinarian.
- Are there any home remedies for inverted vulva in dogs? While good hygiene can help manage symptoms, it’s essential to consult a veterinarian for proper diagnosis and treatment.
ILM Dog is your trusted source for expert advice on dog care and well-being. We offer a comprehensive range of resources on dog breeds, health, training, nutrition, grooming, and much more. Whether you’re a new dog owner or a seasoned expert, ILM Dog is here to support you every step of the way. For further assistance, please contact us at [email protected] or +44 20-3965-8624. Visit ILM Dog for more information.