The hock joint in dogs, often overlooked, plays a crucial role in their mobility and overall well-being. Understanding its structure, function, and potential problems is essential for every dog owner. This article will delve into everything you need to know about the dog hock joint, from its anatomy to common injuries and treatment options.
A dog’s hock joint, located on the hind leg between the paw and the stifle (knee), is a complex structure analogous to the human ankle. It allows for a range of movements, enabling activities like running, jumping, and even simple walking. Proper care and attention to this vital joint can prevent future mobility issues and ensure a happy, active life for your canine companion.
Anatomy of the Canine Hock Joint
The hock joint is a marvel of biological engineering, comprised of multiple bones, ligaments, and tendons working in harmony. The primary bones involved include the tibia, fibula, talus, calcaneus, and the small tarsal bones. These bones are connected by a network of ligaments providing stability and controlling the range of motion. Tendons, attaching muscles to the bones, facilitate movement and power.
Understanding this intricate anatomy is key to recognizing potential problems and seeking appropriate veterinary care.
Common Hock Joint Problems in Dogs
Several conditions can affect a dog’s hock joint, ranging from minor sprains to more serious issues like arthritis and ligament tears. Some common problems include:
- Hyperextension: This occurs when the joint is forced beyond its normal range of motion, often due to trauma or strenuous activity.
- Osteoarthritis: A degenerative joint disease that causes pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. It’s particularly prevalent in older dogs and certain breeds.
- Ligament injuries: Cruciate ligament tears, similar to those seen in humans, can occur in dogs, causing instability and pain.
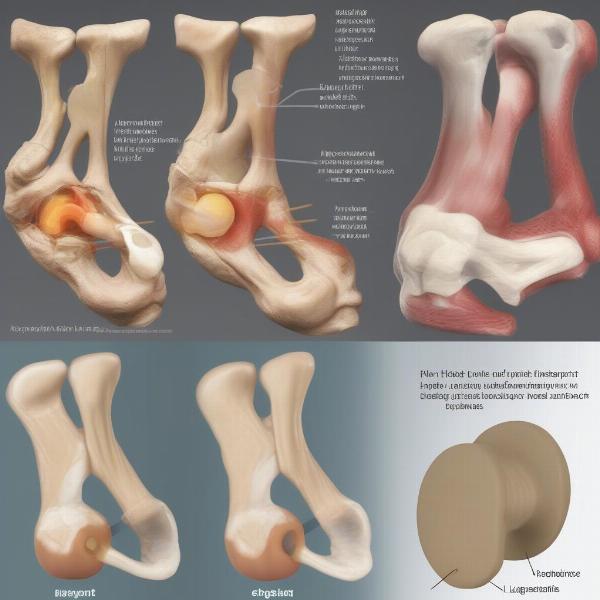 Common Hock Joint Issues in Dogs
Common Hock Joint Issues in Dogs
These conditions can significantly impact a dog’s quality of life, limiting their ability to engage in normal activities. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing these issues and preventing further complications.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Hock Joint Issues
If you suspect your dog is experiencing hock joint pain, consult a veterinarian immediately. They will conduct a thorough physical examination, possibly including x-rays or other imaging techniques, to determine the cause of the problem. Treatment options vary depending on the specific condition and may include:
- Medications: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatories, and joint supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin can help manage pain and inflammation. glucosamine chondroitin msm for dogs
- Bracing or splinting: hock dog brace can provide support and stability to the joint, aiding in healing and pain relief.
- Physical therapy: Exercises and stretches can improve joint flexibility and strength.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair damaged ligaments or address other structural issues. dog swollen hock joint
“Early intervention is crucial for managing hock joint problems,” says Dr. Emily Carter, DVM, a specialist in canine orthopedics. “The sooner we address the issue, the better the chances for a full recovery and improved quality of life for the dog.”
Preventing Hock Joint Problems
While not all hock joint problems are preventable, there are steps you can take to minimize the risk:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight puts extra stress on the joints, increasing the risk of injury and arthritis.
- Regular exercise: Appropriate exercise helps keep the joints healthy and strong. dog pastern
- Provide a supportive environment: Ensure your dog has a comfortable bed and avoid slippery surfaces that can increase the risk of injury.
- Nutritional supplements: Supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin can help support joint health, especially in older dogs. calcaneus dog
By taking these proactive steps, you can help keep your dog’s hock joints healthy and functioning optimally for years to come.
Conclusion
The hock joint is a vital component of a dog’s mobility. Understanding its anatomy, common problems, and preventative measures can help you provide the best possible care for your canine companion. By staying informed and proactive, you can ensure your dog enjoys a happy, active life, free from the limitations of hock joint issues.
FAQ
- What are the signs of hock joint pain in dogs? Signs can include limping, stiffness, swelling, difficulty jumping or climbing stairs, and reluctance to exercise.
- How is a hock joint injury diagnosed? A veterinarian will perform a physical exam and may recommend x-rays or other imaging tests.
- Can hock joint problems be cured? While some conditions can be fully resolved, others, like arthritis, require ongoing management.
- What is the best way to prevent hock joint problems? Maintaining a healthy weight, providing regular exercise, and offering a supportive environment are key.
- What are the long-term effects of untreated hock joint problems? Untreated issues can lead to chronic pain, decreased mobility, and a diminished quality of life.
- Are certain breeds more prone to hock joint problems? Yes, some larger breeds and those genetically predisposed to joint issues are at higher risk.
- What kind of exercises are good for dogs with hock joint problems? Low-impact activities like swimming and controlled leash walks are often recommended.
ILM Dog is your trusted resource for comprehensive information on dog breeds, health, training, nutrition, grooming, and much more. We offer expert advice and practical tips to help you provide the best possible care for your furry friend. For further information and personalized guidance, contact us at [email protected] or call us at +44 20-3965-8624. Visit ILM Dog for all your dog care needs!