The dog scapula, or shoulder blade, plays a crucial role in a dog’s movement and overall well-being. Understanding its anatomy and function can help owners recognize potential problems and provide the best care for their canine companions. This article delves into the intricacies of the dog scapula, covering everything from its structure and common injuries to preventative measures and treatment options.
The scapula is a flat, triangular bone that forms the basis of the shoulder joint. It connects the forelimb to the body and facilitates a wide range of motion, from walking and running to jumping and playing. A healthy scapula is essential for a dog’s mobility and quality of life. Understanding the scapula’s role can help owners make informed decisions regarding their dog’s exercise, nutrition, and overall health.
Dog Scapula Anatomy and Function
The dog scapula is situated on the lateral surface of the thoracic wall. It articulates with the humerus (upper arm bone) to form the shoulder joint. The spine of the scapula, a prominent ridge running down the length of the bone, serves as an attachment point for important muscles that stabilize and move the shoulder. The glenoid cavity, a shallow socket on the lateral angle of the scapula, forms the articulation point with the humerus, allowing for the flexibility and range of motion crucial for a dog’s activities.
The scapula’s primary function is to provide a stable base for the forelimb and facilitate a wide range of movement. The intricate interplay of muscles attached to the scapula allows for flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and rotation of the shoulder joint. This intricate system enables dogs to navigate various terrains, perform agile movements, and participate in their favorite activities.
Common Scapula Injuries in Dogs
While the scapula is relatively protected, injuries can still occur, particularly in active or working dogs. Fractures, although less common than in other bones, can result from trauma such as falls or collisions. scapula in dogs Osteochondrosis, a developmental disease affecting cartilage formation, can also impact the scapula, particularly in larger breeds. Furthermore, muscle strains and tears affecting the muscles surrounding the scapula can cause pain and restrict movement. scapula anatomy dog
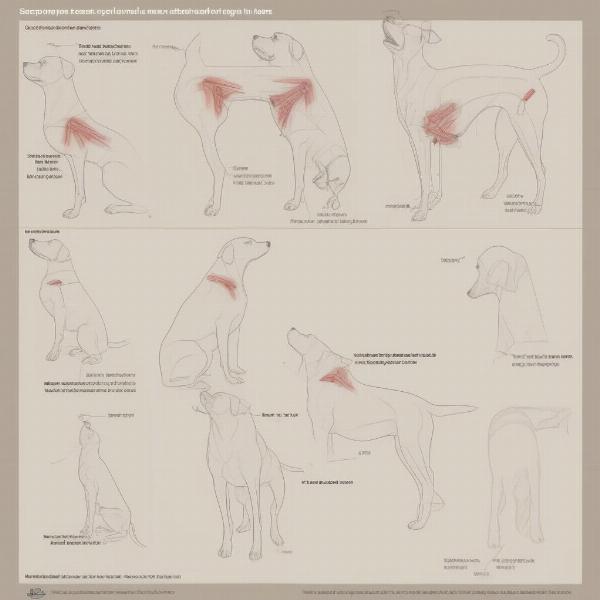 Common Dog Scapula Injuries
Common Dog Scapula Injuries
Diagnosing and Treating Scapula Issues
Diagnosing scapula issues requires a thorough veterinary examination, often involving palpation, manipulation of the shoulder joint, and imaging techniques such as X-rays or CT scans. Treatment varies depending on the specific injury or condition. Fractures may require surgical intervention, while muscle strains often respond well to rest and conservative management. In cases of osteochondrosis, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove damaged cartilage and promote healing.
Preventing Scapula Problems in Your Dog
While not all scapula issues are preventable, certain measures can help reduce the risk. Maintaining a healthy weight for your dog minimizes stress on the shoulder joint. Providing a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients supports bone and muscle health. Regular, controlled exercise strengthens supporting muscles and helps maintain optimal joint function. dog arm Avoiding excessive jumping or high-impact activities, especially in puppies and young dogs, can also protect the developing scapula. german shepherd dog skeleton
Conclusion
The dog scapula is a vital component of their musculoskeletal system, crucial for their mobility and overall well-being. Understanding its anatomy, function, and common issues allows owners to provide proactive care and address potential problems effectively. By following preventative measures and seeking timely veterinary care, you can help your dog maintain a healthy and active lifestyle. real dog skeleton
FAQ
- What are the signs of a scapula injury in a dog? Lameness, reluctance to move the affected leg, swelling or pain around the shoulder area, and changes in gait are common indicators.
- How is a scapula fracture diagnosed? Veterinarians typically use X-rays or CT scans to visualize the fracture and assess its severity.
- Can osteochondrosis of the scapula be treated without surgery? In some mild cases, conservative management with rest and medication may be sufficient. However, surgical intervention is often necessary for more severe cases.
- What is the recovery time for a scapula fracture? Recovery time can vary depending on the severity of the fracture and the treatment method, but it typically takes several weeks to months.
- How can I prevent scapula injuries in my dog? Maintaining a healthy weight, providing a balanced diet, and ensuring regular, controlled exercise are crucial for preventing scapula problems.
- Are certain breeds more prone to scapula issues? Larger breeds, particularly those with rapid growth rates, are at increased risk of developing osteochondrosis.
- What is the long-term prognosis for a dog with a scapula injury? With appropriate treatment and rehabilitation, most dogs can regain full function and enjoy a good quality of life.
ILM Dog is your trusted resource for all things dog-related. From breed selection and health care to training and nutrition, we provide expert advice and practical tips to help you care for your canine companion. We specialize in dog breed information, health and wellness guidance, and product recommendations. For professional support tailored to your dog’s individual needs, contact our team of experts at [email protected] or call us at +44 20-3965-8624. ILM Dog is committed to providing dog owners worldwide with reliable and practical information to ensure the health and happiness of their furry friends.