The canine skeleton, a complex and fascinating structure, plays a crucial role in a dog’s movement, protection of vital organs, and overall well-being. Understanding the dog skeleton anatomy, from the skull to the tail, can help owners provide better care for their furry friends. Whether you’re a seasoned dog owner or just starting your journey, this guide will provide valuable insights into the intricacies of the dog skeleton.
A dog’s skeleton is more than just a framework; it’s a dynamic system that supports the body, allows for a range of motion, and protects vital organs like the heart and lungs. The skeleton also plays a key role in blood cell production and mineral storage. Knowing the basic anatomy of your dog’s skeletal system can help you understand their movements, potential vulnerabilities, and overall health.
Major Bones in a Dog’s Skeleton
The dog skeleton is comprised of approximately 319 bones, the number varying slightly depending on the breed and the presence or absence of the dewclaws. These bones are broadly categorized into the axial and appendicular skeletons. The axial skeleton consists of the skull, vertebral column, ribs, and sternum. The appendicular skeleton includes the limbs and their connecting girdles.
The Skull
The skull houses the brain and essential sensory organs. It’s divided into two main parts: the cranium and the facial bones. The shape and size of the skull vary considerably between breeds, contributing to the diverse appearances we see in the dog world.
The Vertebral Column
The vertebral column, or spine, runs from the base of the skull to the tip of the tail, providing flexibility and support. It’s made up of individual vertebrae categorized into cervical (neck), thoracic (chest), lumbar (lower back), sacral (pelvic), and caudal (tail) regions.
Ribs and Sternum
The ribs, attached to the thoracic vertebrae, form a protective cage around the chest cavity. They safeguard vital organs such as the heart and lungs. The sternum, commonly known as the breastbone, connects the ribs ventrally.
Limbs and Girdles
The appendicular skeleton includes the forelimbs (front legs) and hindlimbs (back legs). The forelimbs are attached to the body via the pectoral girdle (shoulder), while the hindlimbs connect through the pelvic girdle (hip).
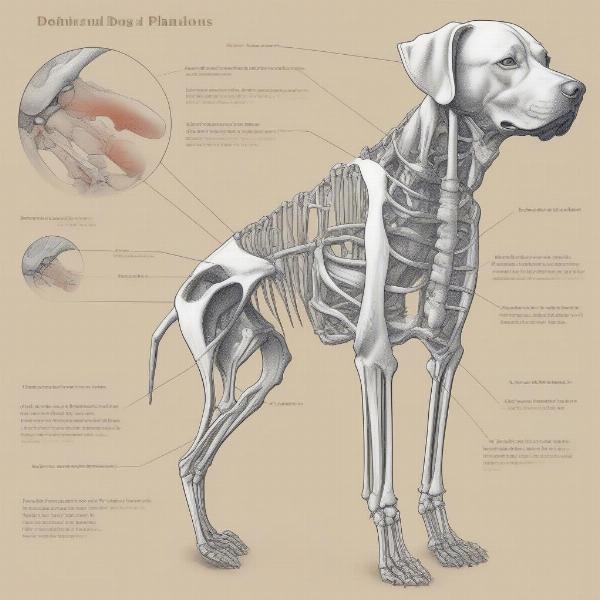 dog-forelimb-skeleton
dog-forelimb-skeleton
Importance of Understanding Dog Skeletal Anatomy
Understanding the anatomy of a dog’s skeleton offers several benefits for owners:
- Recognizing Potential Health Issues: Knowing the normal structure of bones can help you identify potential problems such as fractures, dislocations, or developmental abnormalities.
- Supporting Proper Growth and Development: Especially crucial in puppies, understanding skeletal development can guide you in providing appropriate nutrition and exercise.
- Choosing the Right Exercise: Different breeds have varying skeletal structures, impacting their suitability for certain activities. For example, breeds with long backs, like Dachshunds, are prone to back problems and should avoid strenuous jumping or twisting activities. You can find more information about the Dachshund skeleton at dachshund dog skeleton.
- Understanding Breed-Specific Predispositions: Certain breeds are more susceptible to specific skeletal issues. Knowing these predispositions allows for early detection and preventive measures. Interested in how many bones a dog has? Check out this article: how many bones are in a dog.
- Interpreting Veterinary Diagnoses: Familiarity with skeletal terminology can help you better understand your veterinarian’s explanations and recommendations.
“Understanding the skeletal structure is fundamental to providing optimal care for your canine companion,” says Dr. Emily Carter, a renowned veterinary orthopedic surgeon. “It allows owners to be proactive in preventing injuries and recognizing potential health issues early on.”
Conclusion
The dog skeleton, a marvel of biological engineering, is more than just a collection of bones. It’s a dynamic and crucial system that underpins a dog’s health and well-being. By understanding the basic anatomy and the importance of the dog skeleton, owners can make informed decisions about their dog’s care, exercise, and overall lifestyle. Want to learn more about a real dog skeleton? Visit real dog skeleton. If your dog likes to snuggle, you might be interested in why does my dog burrow into me. For those looking for unique home decor, check out dog skeleton decoration.
ILM Dog is your trusted resource for all things canine. We offer expert advice on dog breeds, health, training, nutrition, grooming, and much more. Whether you’re a new dog owner or a seasoned pro, our comprehensive resources will help you provide the best possible care for your furry friend. Contact us today for personalized guidance and support. Email: [email protected], Phone: +44 20-3965-8624. Visit ILM Dog for more information.